Explain Two Different Methods of Pollen Transfer in Angiosperms
I Receptivity of pollen release and stigma is not synchronized ie either the pollen is released before the stigma becomes receptive or stigma becomes receptive before the release of pollen. Different agents can transfer pollen grains from anther of one flower to the stigma of other flowers.

Similarities And Differences Between Pollen And Seeds 1 Reserves Are Download Scientific Diagram
In angiosperms the transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of the flower of the same or another plant is known as pollination.

. One of the male gametes moves towards the egg cell and fuses with it to form zygoteiii. Slugs snails and squirrels malacophily. Diploid and are made when haploid gametes join in fertilization B.
Wind pollination is derived in angiosperms and has developed independently in several different groups. It should be noted that pollination simply means the process of transferring pollen from the anthers to the stigma. The ways of dispersing fruits can be through pollen dispersal such as insects and birds spreading the pollen of flowers for reproduction.
In angiosperms pollination is defined as the placement or transfer of pollen from the anther to the stigma of the same flower or another flower. It should be noted that birds and insects are pollinators and can spread angiosperm. In angiosperms pollen grains are A.
Upon transfer the pollen germinates to form the pollen tube and the sperm for fertilizing the egg. The male reproductive organ in the angiosperms is the stamen. In Angiosperms five different types of pollen tetrads can be formed.
Chapter 38 Angiosperm Reproduction and Biotechnology 381 Q. Explain the adaptive advantage of double fertilization in angiosperms. Inside the anthers microsporangia male gametophytes divide by meiosis to generate haploid microspores which in turn undergo mitosis and give rise to pollen grains.
It is transported by air currents to the ovule micropyle. There are different types of pollination based on the pollinating agents. One sperm fertilizes egg to form zygote and other sperm combines with two polar nuclei to form endosperm.
See if you can identify the reason for this as you read through the steps for fertilisation. Gymnosperm pollen is produced by pollen sacs in male cones. Pick one of the methods and explain how it functions in prohibiting self-fertilization.
Each type of pollination has its own merits. When the pollen grains fall on the stigma the pollen tube enters one of the synergids and releases two male gametesii. Haploid and are made.
Double fertilization is an event unique to angiosperms. It cannot occur until after the growth of the pollen tube from the pollen grain. This is termed as triple fusioniv.
Each pollen grain contains two cells. Xenogamy is the cross-pollination where the pollen grain transfer occurs across flowers of two different plants. Angiosperm cycle and what aspects about angiosperms promote the transfer.
Only three microspores are observed when we view from one side and the fourth microspore is at the backside. Haploid and are made when haploid spores undergo mitosis D. In gymnosperms pollination involves pollen transfer from the male cone to the female cone.
They help carry pollen from one flower to another 7. The process of fertilisation in plants occurs in clearly defined steps. Pollen may be dispersed as single grains as in many plants relying on wind dispersal or in groups of grains as in almost all zoophilous species.
In angiosperms pollination is the transfer of pollen from an anther to a stigma. The angiosperm life cycle is dominated by the sporophyte stage. Gymnosperms provide many useful products Paper.
Based on differences in pollen types between the two species we established that pollen loads carried by honey bees were between 67 and 99 species-specific whereas pollen. Reproduction in angiosperms Pollen falls on the stigma from the anther Sperm from the pollen fertilized the egg in the ovule Seed develops Ovary swells and grows around the seed as a fruit 8. It is defined as the transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of the same flower in the same plant.
In other words the transfer of pollen from the anther of one plant to the stigma of another plant. For example within the aster family wind pollination accompanied by floral reduction Effective pollination involves the transfer of pollen from the anthers to a stigma of the same species and subsequent germination and growth of the pollen tube to the micropyle of the ovule. In angiosperms each pollen grain contains two male sex cells.
One generative cell that will divide into two sperm and a second cell that will become the pollen tube cell. The other male gamete fuses with the two polar nuclei and forms the primary endosperm nucleus. One sperm in the pollen fertilizes the egg forming a diploid zygote while the other combines with the two polar nuclei forming a triploid cell that develops into a food storage tissue called the endosperm.
It is defined as the transfer of pollen grains from the anther of one flower to the stigma of another flower on the same plant. There are usually two different cones. Pollen dispersal in clumps is typical of angiosperms.
Xenogamy leads to a new variety whereas autogamy helps to preserve parental characters. Pollen tube discharges two sperm into embryo sac. In angiosperms pollen is transported either singly or in packets of variable number pollen loads that are the equivalent of an ejaculate and pollen from several males can be deposited on a stigma via abiotic or biotic pollinating agents leading to pollen competition mixed-donor pollination.
Ii In some other species the anther and stigma are placed at different positions so that the pollen cannot come in contract with the stigma of same flower which will prevent autogamy. Male cones produce pollen Female cones contain an ovule Pine Cones Male Cone Female Cone 4. Diploid and are made when haploid gametophytes join in pollination C.
Explain pollen tube growth and embryo sac development and how the two form an embryo. Fertilization is the fusion of the egg and sperm to form the zygote. The anther is present at the.
A Explain post pollination events leading to seed production in angiospermsb List the different types of pollination depending on the source of pollen grain 5 Login. Explain the plant photoreceptors and how they tell the cell to start the greening process. Distinguish between pollination and fertilization.
Pollination is A transfer of pollen from the male reproductive structure to the female After pollination the egg is fertilized and seeds are dispersed by the wind 5. After the pollen grain lands on the mature stigma of a flower from the same species the pollen produces a tube.

Pollinator Party Pollination Infographic On Behance Pollination Infographic Human Body Systems Projects
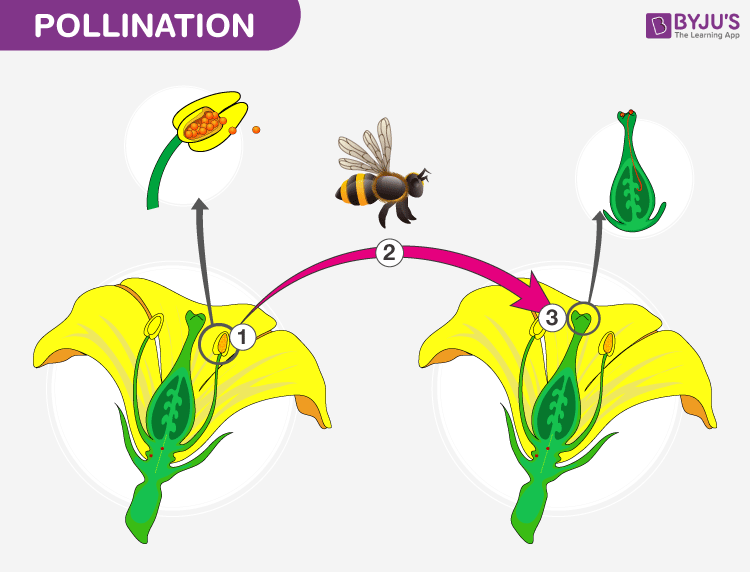
Pollination Types Self And Cross Pollination Pollinating Agents

The Key Difference Between Synergid And Egg Cell Is That The Synergid Cell Is One Of The Two Cells That Accompanies The Egg Cell Wh Pollen Fertility Generative

Angiosperm Pollination Britannica

The Types And Methods Of Pollination In The Plants Science Online

Pollination Its Types And Comparisons Between Self And Cross Pollination

Pollen Tube Growth In The Pistil A Schematic Diagram Of Pollen Download Scientific Diagram
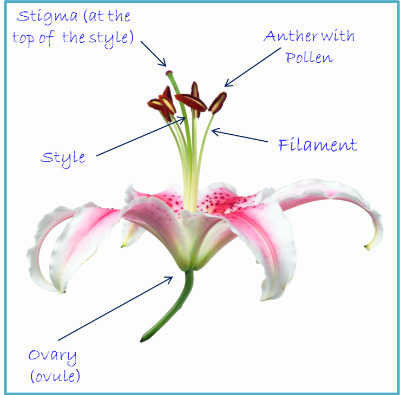
No comments for "Explain Two Different Methods of Pollen Transfer in Angiosperms"
Post a Comment